Settings
Note
If you're unsure about what "Django settings" are, you can refer to How to Edit Django Settings in OpenWISP for guidance.
OPENWISP_SSH_AUTH_TIMEOUT
type: |
|
default: |
|
unit: |
|
Configure timeout to wait for an authentication response when establishing a SSH connection.
OPENWISP_SSH_COMMAND_TIMEOUT
type: |
|
default: |
|
unit: |
|
Configure timeout on blocking read/write operations when executing a command in a SSH connection.
OPENWISP_SSH_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT
type: |
|
default: |
|
unit: |
|
Configure timeout for the TCP connect when establishing a SSH connection.
OPENWISP_CONNECTORS
type: |
|
default: |
|
Available connector classes. Connectors are python classes that specify ways in which OpenWISP can connect to devices in order to launch commands.
OPENWISP_UPDATE_STRATEGIES
type: |
|
default: |
|
Available update strategies. An update strategy is a subclass of a
connector class which defines an update_config method which is in
charge of updating the configuration of the device.
This operation is launched in a background worker when the configuration of a device is changed.
It's possible to write custom update strategies and add them to this setting to make them available in OpenWISP.
OPENWISP_CONFIG_UPDATE_MAPPING
type: |
|
default: |
|
A dictionary that maps configuration backends to update strategies in order to automatically determine the update strategy of a device connection if the update strategy field is left blank by the user.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_BACKENDS
type: |
|
default: |
|
Available configuration backends. For more information, see netjsonconfig backends.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_VPN_BACKENDS
type: |
|
default: |
|
Available VPN backends for VPN Server objects. For more information, see netjsonconfig VPN backends.
A VPN backend must follow some basic rules in order to be compatible with openwisp-controller:
it MUST allow at minimum and at maximum one VPN instance
the main NetJSON property MUST match the lowercase version of the class name, e.g.: when using the
OpenVpnbackend, the system will look intoconfig['openvpn']it SHOULD focus on the server capabilities of the VPN software being used
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_DEFAULT_BACKEND
type: |
|
default: |
|
The preferred backend that will be used as initial value when adding new
Config or Template objects in the admin.
This setting defaults to the raw value of the first item in the
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_BACKENDS setting, which is
netjsonconfig.OpenWrt.
Setting it to None will force the user to choose explicitly.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_DEFAULT_VPN_BACKEND
type: |
|
default: |
|
The preferred backend that will be used as initial value when adding new
Vpn objects in the admin.
This setting defaults to the raw value of the first item in the
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_VPN_BACKENDS setting, which is
openwisp_controller.vpn_backends.OpenVpn.
Setting it to None will force the user to choose explicitly.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_REGISTRATION_ENABLED
type: |
|
default: |
|
Whether devices can automatically register through the controller or not.
This feature is enabled by default.
Auto-registration must be supported on the devices in order to work, see openwisp-config automatic registration for more information.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_CONSISTENT_REGISTRATION
type: |
|
default: |
|
Whether devices that are already registered are recognized when reflashed or reset, hence keeping the existing configuration without creating a new one.
This feature is enabled by default.
Auto-registration must be enabled also on the devices in order to work, see openwisp-config consistent key generation for more information.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_REGISTRATION_SELF_CREATION
type: |
|
default: |
|
Whether devices that are not already present in the system are allowed to register or not.
Turn this off if you still want to use auto-registration to avoid having to manually set the device UUID and key in its configuration file but also want to avoid indiscriminate registration of new devices without explicit permission.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_CONTEXT
type: |
|
default: |
|
Additional context that is passed to the default context of each device object.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_CONTEXT can be used to define system-wide
configuration variables.
Important
After modifying the system-defined variables in
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_CONTEXT, clear the cache to ensure that
devices, templates, and VPN receive the updated configuration values:
cd /opt/openwisp2
python manage.py clear_cache
System-defined variables can be referenced in VPN, Template, and Config objects. When these variables are updated, existing cached configurations that depend on them do not automatically reflect the new values. Consequently, devices may continue using outdated configurations unless the cache is cleared.
For more information regarding how to use configuration variables in OpenWISP, refer to Configuration Variables.
For technical information about how variables are handled in the lower levels of OpenWISP, see netjsonconfig context: configuration variables.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_DEFAULT_AUTO_CERT
type: |
|
default: |
|
The default value of the auto_cert field for new Template objects.
The auto_cert field is valid only for templates which have type
set to VPN and indicates whether configuration regarding the VPN
tunnel is provisioned automatically to each device using the template,
e.g.:
when using OpenVPN, new x509 certificates will be generated automatically using the same CA assigned to the related VPN object
when using WireGuard, new pair of private and public keys (using Curve25519) will be generated, as well as an IP address of the subnet assigned to the related VPN object
when using VXLAN tunnels over Wireguard, in addition to the configuration generated for Wireguard, a new VID will be generated automatically for each device if the configuration option "auto VNI" is turned on in the VPN object
All these auto generated configuration options will be available as template variables.
The objects that are automatically created will also be removed when they are not needed anymore (e.g.: when the VPN template is removed from a configuration object).
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_CERT_PATH
type: |
|
default: |
|
The file system path where x509 certificate will be installed when
downloaded on routers when auto_cert is being used (enabled by
default).
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_COMMON_NAME_FORMAT
type: |
|
default: |
|
Defines the format of the common_name attribute of VPN client
certificates that are automatically created when using VPN templates which
have auto_cert set to True. A unique slug generated using
shortuuid is appended to
the common name to introduce uniqueness. Therefore, resulting common names
will have {OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_COMMON_NAME_FORMAT}-{unique-slug}
format.
Note
If the name and mac address of the device are equal, the
name of the device will be omitted from the common name to avoid
redundancy.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_MANAGEMENT_IP_DEVICE_LIST
type: |
|
default: |
|
In the device list page, the column IP will show the management_ip
if available, defaulting to last_ip otherwise.
If this setting is set to False the management_ip won't be shown
in the device list page even if present, it will be shown only in the
device detail page.
You may set this to False if for some reason the majority of your user
doesn't care about the management ip address.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_CONFIG_BACKEND_FIELD_SHOWN
type: |
|
default: |
|
This setting toggles the backend fields in add/edit pages in Device
and Template configuration, as well as the backend field/filter in
Device list and Template list.
If this setting is set to False these items will be removed from the
UI.
Note
This setting affects only the configuration backend and NOT the VPN backend.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_DEVICE_NAME_UNIQUE
type: |
|
default: |
|
This setting conditionally enforces unique Device names in an Organization. The query to enforce this is case-insensitive.
Note: For this constraint to be optional, it is enforced on an application level and not on database.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_HARDWARE_ID_ENABLED
type: |
|
default: |
|
The field hardware_id can be used to store a unique hardware id, for
example a serial number.
If this setting is set to True then this field will be shown first in
the device list page and in the add/edit device page.
This feature is disabled by default.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_HARDWARE_ID_OPTIONS
type: |
|
default: |
|
Options for the model field hardware_id.
blank: whether the field is allowed to be blanknull: whether an empty value will be stored asNULLin the databasemax_length: maximum length of the fieldunique: whether the value of the field must be uniqueverbose_name: text for the human readable label of the fieldhelp_text: help text to be displayed with the field
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_HARDWARE_ID_AS_NAME
type: |
|
default: |
|
When the hardware ID feature is enabled, devices will be referenced with their hardware ID instead of their name.
If you still want to reference devices by their name, set this to
False.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_DEVICE_VERBOSE_NAME
type: |
|
default: |
|
Defines the verbose_name attribute of the Device model, which is
displayed in the admin site. The first and second element of the tuple
represent the singular and plural forms.
For example, if we want to change the verbose name to "Hotspot", we could write:
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_DEVICE_VERBOSE_NAME = ("Hotspot", "Hotspots")
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_HIDE_AUTOMATICALLY_GENERATED_SUBNETS_AND_IPS
type: |
|
default: |
|
Setting this to True will hide subnets and IP addresses generated by
subnet division rules from being displayed
in the list of Subnets and IP addresses in the admin dashboard.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_SUBNET_DIVISION_TYPES
type: |
|
default: |
|
Available types for Subject Division Rule objects.
For more information on how to write your own types, please refer to: Custom Subnet Division Rule Types.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_API
type: |
|
default: |
|
Indicates whether the API for Openwisp Controller is enabled or not. To
disable the API by default add OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_API = False in your
project settings.py file.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_API_HOST
type: |
|
default: |
|
Allows to specify backend URL for API requests, if the frontend is hosted separately.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_USER_COMMANDS
type: |
|
default: |
|
Allows to specify a list of tuples for adding commands as described in
the section: Defining New Options in the Commands Menu.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_ORGANIZATION_ENABLED_COMMANDS
type: |
|
default: |
|
This setting controls the command types that are enabled on the system By default, all command types are enabled to all the organizations, but it's possible to disable a specific command for a specific organization as shown in the following example:
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_ORGANIZATION_ENABLED_COMMANDS = {
"__all__": "*",
# Organization UUID: # Tuple of enabled commands
"7448a190-6e65-42bf-b8ea-bb6603e593a5": ("reboot", "change_password"),
}
In the example above, the organization with UUID
7448a190-6e65-42bf-b8ea-bb6603e593a5 will allow to send only commands
of type reboot and change_password, while all the other
organizations will have all command types enabled.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_DEVICE_GROUP_SCHEMA
type: |
|
default: |
|
Allows specifying JSONSchema used for validating the meta-data of Device Groups.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_MANAGEMENT_IP_ONLY
type: |
|
default: |
|
By default, only the management IP will be used to establish connection with the devices.
If the devices are connecting to your OpenWISP instance using a shared
layer2 network, hence the OpenWSP server can reach the devices using the
last_ip field, you can set this to False.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_DSA_OS_MAPPING
type: |
|
default: |
|
OpenWISP Controller can figure out whether it should use the new OpenWrt
syntax for DSA interfaces (Distributed Switch Architecture) introduced in
OpenWrt 21 by reading the os field of the Device object. However,
if the firmware you are using has a custom firmware identifier, the system
will not be able to figure out whether it should use the new syntax and it
will default to OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_DSA_DEFAULT_FALLBACK.
If you want to make sure the system can parse your custom firmware identifier properly, you can follow the example below.
For the sake of the example, the OS identifier MyCustomFirmware 2.0
corresponds to OpenWrt 19.07, while MyCustomFirmware 2.1
corresponds to OpenWrt 21.02. Configuring this setting as indicated
below will allow OpenWISP to supply the right syntax automatically.
Example:
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_DSA_OS_MAPPING = {
"netjsonconfig.OpenWrt": {
# OpenWrt >=21.02 configuration syntax will be used for
# these OS identifiers.
">=21.02": [r"MyCustomFirmware 2.1(.*)"],
# OpenWrt <=21.02 configuration syntax will be used for
# these OS identifiers.
"<21.02": [r"MyCustomFirmware 2.0(.*)"],
}
}
Note
The OS identifier should be a regular expression as shown in above example.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_DSA_DEFAULT_FALLBACK
type: |
|
default: |
|
The value of this setting decides whether to use DSA syntax (OpenWrt >=21 configuration syntax) if openwisp-controller fails to make that decision automatically.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_GROUP_PIE_CHART
type: |
|
default: |
|
Allows to show a pie chart like the one in the screenshot.
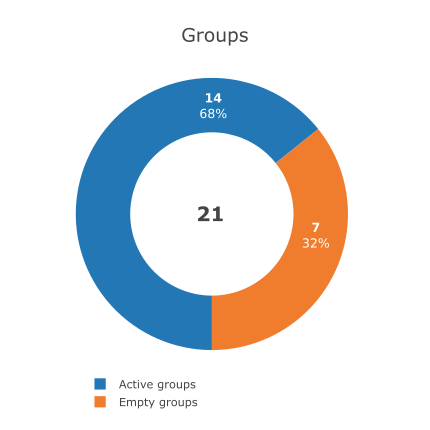
Active groups are groups which have at least one device in them, while empty groups do not have any device assigned.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_API_TASK_RETRY_OPTIONS
type: |
|
default: |
see below |
# default value of OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_API_TASK_RETRY_OPTIONS:
dict(
max_retries=5, # total number of retries
retry_backoff=True, # exponential backoff
retry_backoff_max=600, # 10 minutes
retry_jitter=True, # randomness into exponential backoff
)
This setting is utilized by background API tasks executed by ZeroTier VPN servers and ZeroTier VPN clients to handle recoverable HTTP status codes such as 429, 500, 502, 503, and 504.
These tasks are retried with a maximum of 5 attempts with an exponential backoff and jitter, with a maximum delay of 10 minutes.
This feature ensures that ZeroTier Service API calls are resilient to recoverable failures, improving the reliability of the system.
For more information on these settings, you can refer to the the celery documentation regarding automatic retries for known errors.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_WHOIS_ENABLED
type: |
|
default: |
|
Allows enabling the optional WHOIS Lookup feature.

After enabling this feature, you have to set OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_WHOIS_GEOIP_ACCOUNT and OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_WHOIS_GEOIP_KEY.
Warning
If these three settings are not configured as expected, an
ImproperlyConfigured exception will be raised.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_WHOIS_GEOIP_ACCOUNT
type: |
|
default: |
|
MaxMind Account ID required for the WHOIS Lookup feature.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_WHOIS_GEOIP_KEY
type: |
|
default: |
|
MaxMind License Key required for the WHOIS Lookup feature.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_WHOIS_REFRESH_THRESHOLD_DAYS
type: |
|
default: |
|
Specifies the number of days after which the WHOIS information for a device is considered stale and eligible for refresh.
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_ESTIMATED_LOCATION_ENABLED
type: |
|
default: |
|
Allows enabling the optional Estimated Location feature.
Warning
OPENWISP_CONTROLLER_WHOIS_ENABLED must be set to True before
enabling this feature. Enabling estimated locations while
WHOIS_ENABLED=False will raise ImproperlyConfigured at startup
time.
