Architecture
A typical OpenWISP installation is made of multiple components (e.g. application servers, background workers, web servers, database, messaging queue, VPN server, etc. ) that have different scaling requirements.
The aim of Docker OpenWISP is to allow deploying OpenWISP in cloud based environments which allow potentially infinite horizontal scaling. That is the reason for which there are different docker images shipped in this repository.
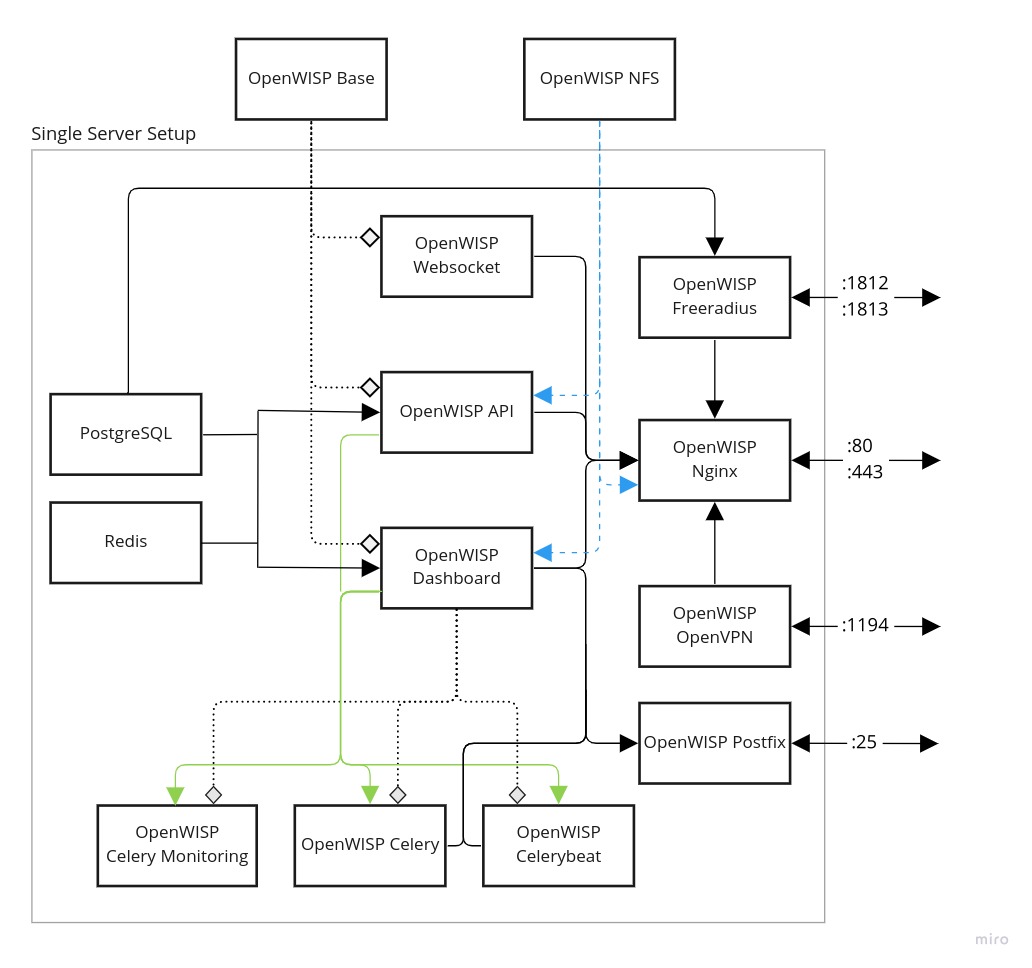
openwisp-dashboard: Your OpenWISP device administration dashboard.
openwisp-api: HTTP API from various OpenWISP modules which can be scaled simply by having multiple API containers as per requirement.
openwisp-websocket: Dedicated container for handling websocket requests, e.g. for updating location of mobile network devices.
openwisp-celery: Runs all the background tasks for OpenWISP, e.g. updating configurations of your device.
openwisp-celery-monitoring: Runs background tasks that perform active monitoring checks, e.g. ping checks and configuration checks. It also executes task for writing monitoring data to the timeseries DB.
openwisp-celerybeat: Runs periodic background tasks. e.g. revoking all the expired certificates.
openwisp-nginx: Internet facing container that facilitates all the HTTP and Websocket communication between the outside world and the service containers.
openwisp-freeradius: Freeradius container for OpenWISP.
openwisp-openvpn: OpenVPN container for out-of-the-box management VPN.
openwisp-postfix: Mail server for sending mails to MTA.
openwisp-nfs: NFS server that allows shared storage between different machines. It does not run in single server machines but provided for K8s setup.
openwisp-base: It is the base image which does not run on your server, but openwisp-api & openwisp-dashboard use it as a base.
Redis: data caching service (required for actions like login).
PostgreSQL: SQL database container for OpenWISP.